Safety Data
Most common AEs—adult
Most adverse events (AEs) were reported to be mild or moderate1
The safety profile of BRIVIACT was established in 12-week, Phase 3, adult, placebo-controlled trials2
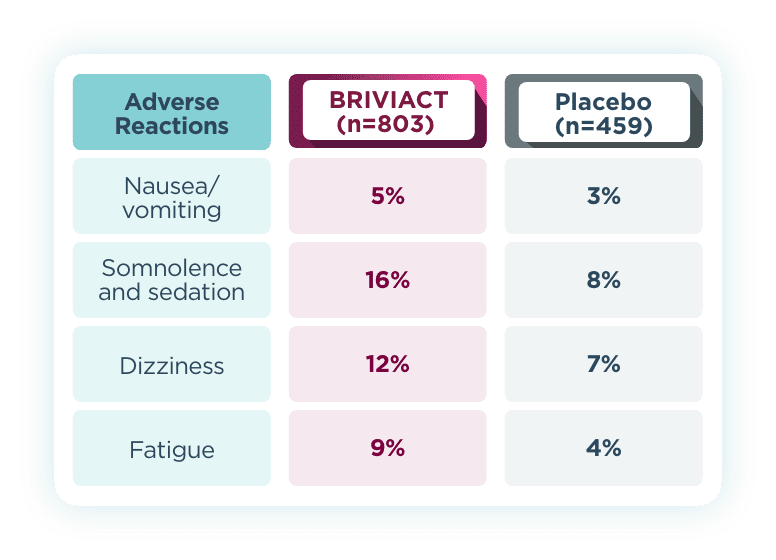
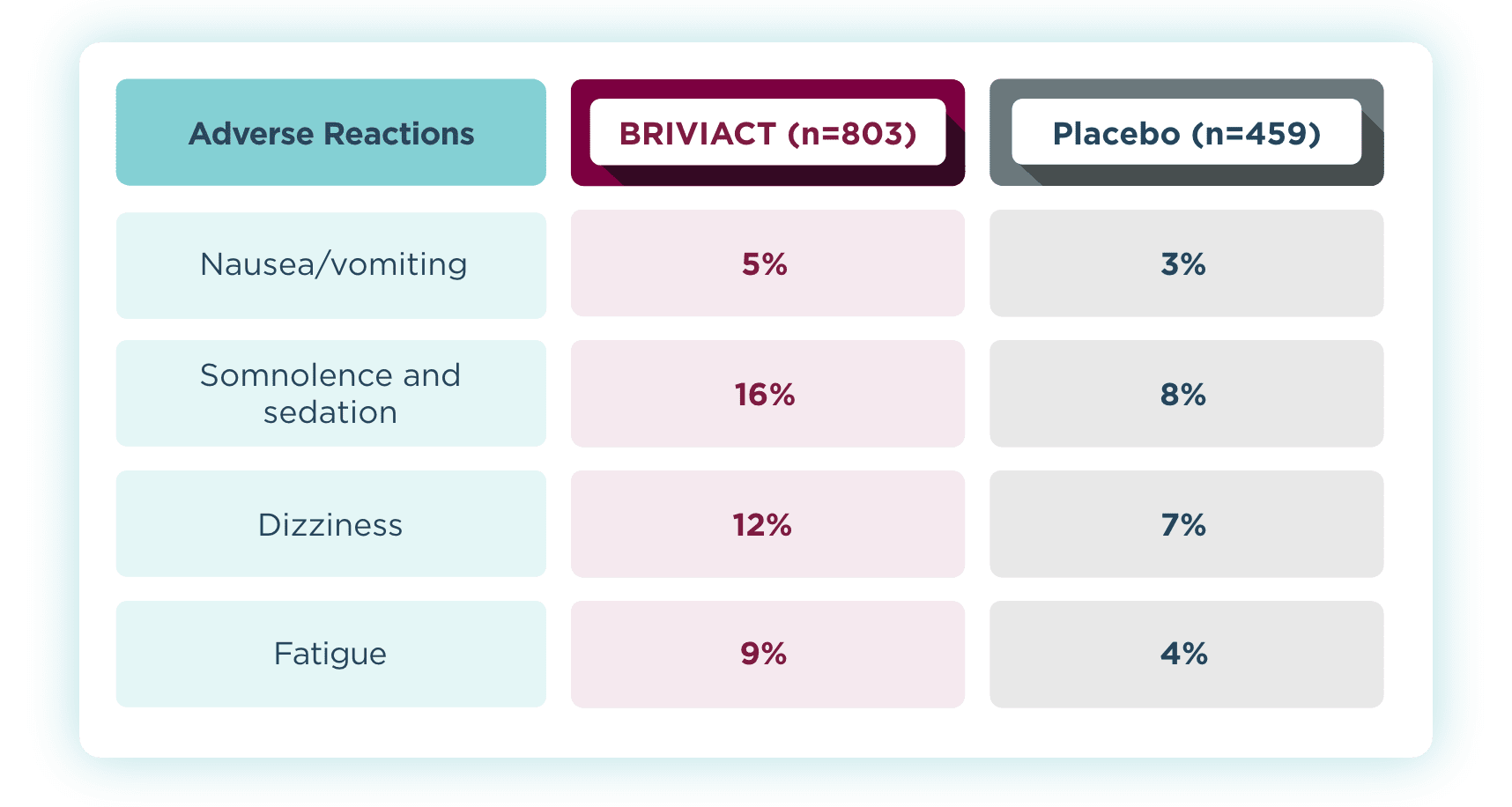
Most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% for BRIVIACT
and at least 2% more than placebo2
- Behavior-related adverse reactions were not common for BRIVIACT in adult pivotal trials2
- 1.7% of adult patients treated with BRIVIACT discontinued treatment because of psychiatric
reactions compared to 1.3% of patients who received placebo2
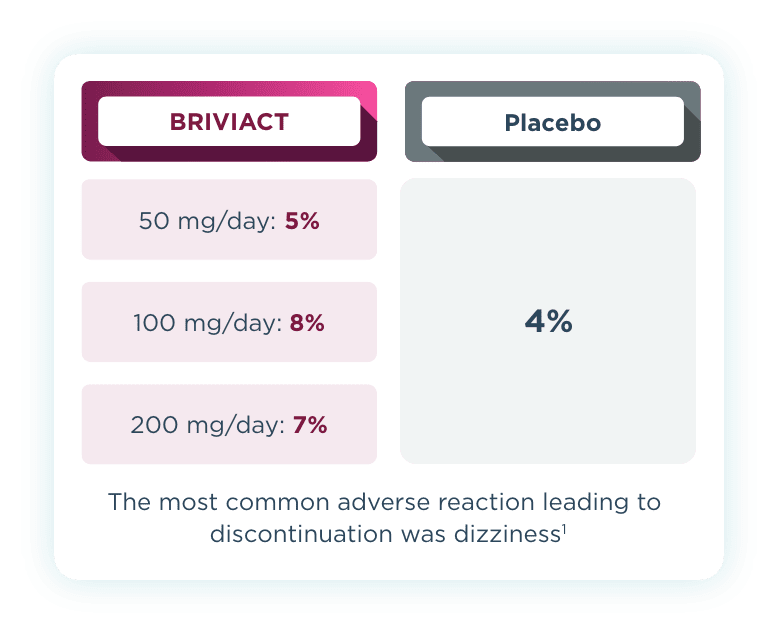
Discontinuation rates
Across all 3 trials, low discontinuation rates due to adverse events were observed2

Most common AEs—pediatric
BRIVIACT was generally well tolerated for infants 1 month of age and older1
The safety profile for pediatric patients was similar to adults2
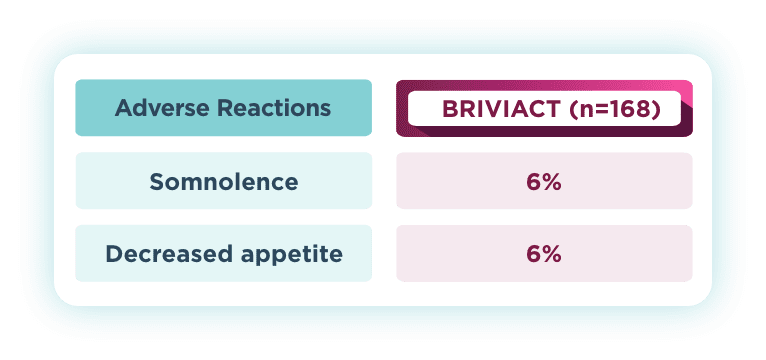
The most common drug-related TEAEs in pooled pediatric studies (≥5%)1

Pooled safety data from Phase 2a and Phase 3a open-label trials of BRIVIACT in patients aged 1 month to <17 years (N=219), uncontrolled by 1 to 3 ASMs. Of the 219 patients, 168 had focal seizures. After dose adjustment, patients received BRIVIACT 1 to 5 mg/kg/day (maximum 200 mg/day).
ASM=antiseizure medication; TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event.
IV safety & tolerability
BRIVIACT injection safety and tolerability is consistent with oral formulations2
•
The safety and tolerability of BRIVIACT IV have been evaluated as a 15-minute infusion or a bolus (up to 2-minute) injection in an open-label study in children aged 2 months to <16 years with epilepsy1,2
•
The safety and pharmacokinetics of BRIVIACT were similar in the infusion and bolus injection groups1
•
Adverse reactions with BRIVIACT injection in adult and pediatric patients were generally similar to those observed with BRIVIACT tablets. Other adverse events that occurred in adult patients who received BRIVIACT injection included dysgeusia, euphoric mood, feeling drunk, and infusion site pain2
DDI incidence
BRIVIACT has a low incidence of drug interactions with other ASMs2
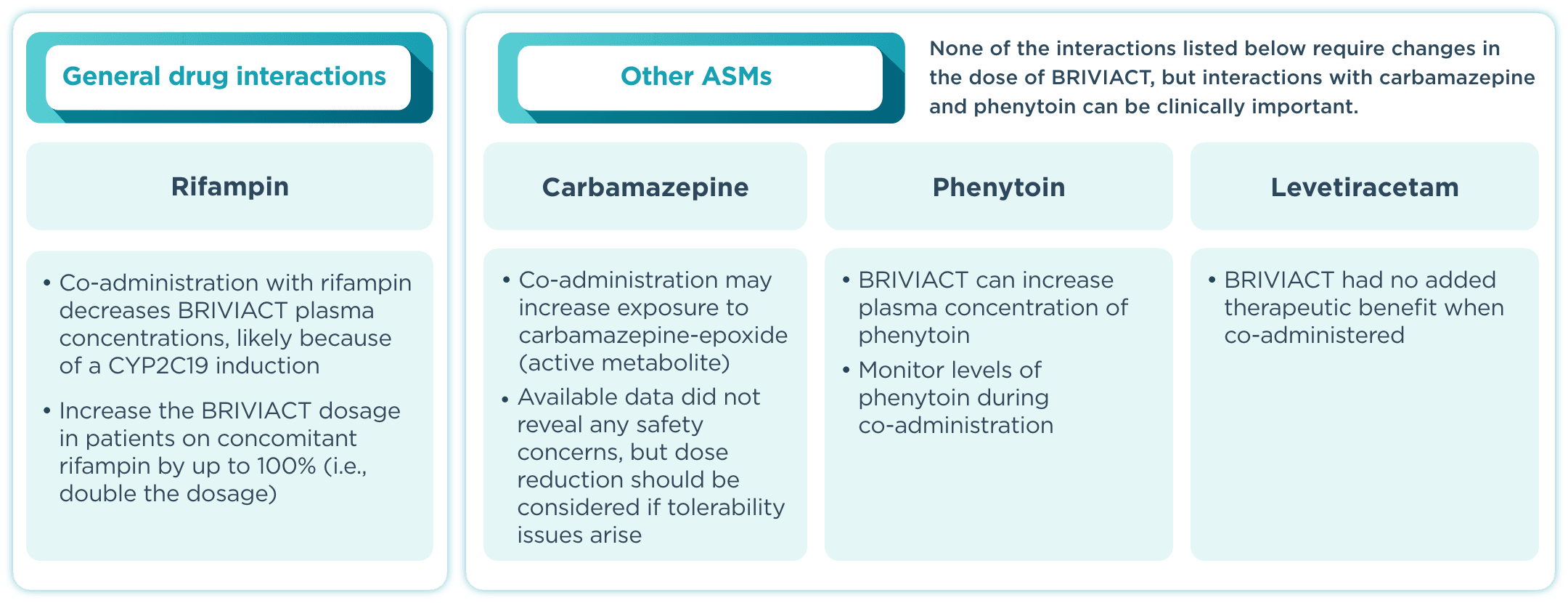
DDI=drug-drug interaction; IV=intravenous.
References: 1. Data on file. UCB, Inc. 2. BRIVIACT® (brivaracetam) prescribing information. Smyrna, GA: UCB, Inc. 3. Patel AD, Badalamenti V, Gasalla T, Elmoufti S, Elshoff JP. Safety and tolerability of adjunctive brivaracetam in children with focal seizures: interim analysis of pooled data from two open-label trials. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2020;25:68-76. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2019.11.007